More UIKit
More UIKit
1. Introduction to UITableView and UICollectionView in UIKit
UITableView and UICollectionView are vital for displaying scrollable lists or grids in iOS apps. They use reusable cells for performance:
- UITableView: Typically a vertical, single-column list (e.g., contacts, settings).
- UICollectionView: A flexible, multi-column or custom layout approach (e.g., grids, carousels).
Both rely on:
- Data Source: Provides the “what” – the number of items and how each cell is configured.
- Delegate: Provides the “how” – user interactions, selection, layout, etc.
2. How to Add These in a XIB
In this guide, we’ll create two example view controllers:
FruitsViewControllerwith a UITableView.ColorGridViewControllerwith a UICollectionView.
2.1. Create a XIB + Swift Class for a Table View
- In Xcode, File → New → File from Template
- Under iOS, select “Cocoa Touch Class” (or “Swift File + XIB”).
- Name it
FruitsViewController. Make sure Subclass of isUIViewController. - Check “Also create XIB” if available. If not, create the
.xibmanually:- File → New → File… → View and name it
FruitsViewController.xib.
- File → New → File… → View and name it
- Open
FruitsViewController.xib.- Select the top-level View.
- Identity Inspector → Class =
FruitsViewController.
2.2. Drag a UITableView Onto the XIB
- Search for “Table View” in the Object Library.
- Drag it onto the main view.
- Use Auto Layout constraints (pin top, left, right, bottom = 0) so it fills the screen.
2.3. Create an IBOutlet for the Table View
- Open the Assistant Editor or Ctrl-drag from the Table View in the XIB to
FruitsViewController.swift. -
Create:
@IBOutlet weak var tableView: UITableView!
2.4. Set a Reuse Identifier for the Prototype Cell
-
In the
viewDidLoad(), register the prototype cell for the Table View.tableView.register(UITableViewCell.self, forCellReuseIdentifier: "FruitCell")
3. Configure These in Code
Now we’ll set up the FruitsViewController to show a list of fruits using UITableView.
FruitsViewController.swift might look like this:
import UIKit
class FruitsViewController: UIViewController {
// 1) Connect the IBOutlet from the XIB
@IBOutlet weak var tableView: UITableView!
// 2) Create a sample data array
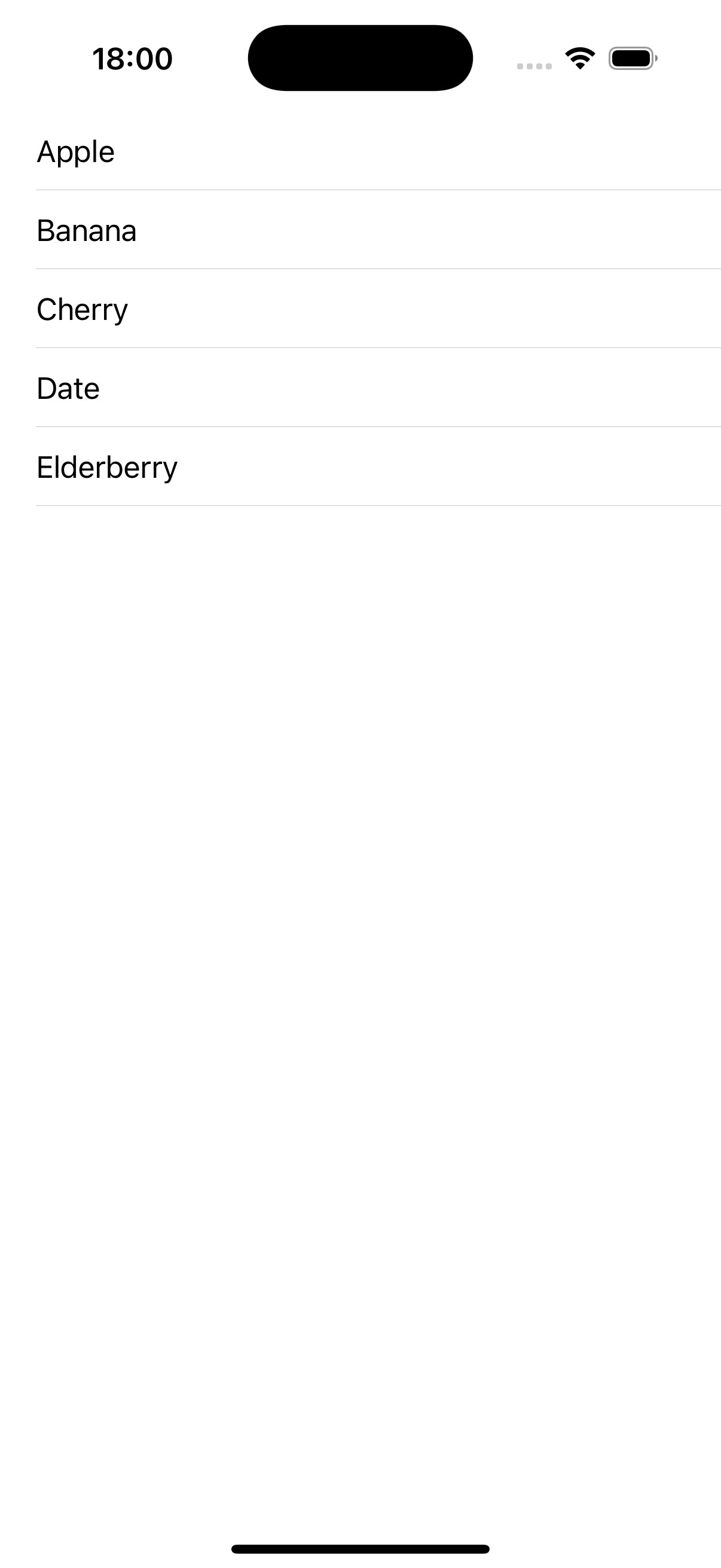
private let fruits = ["Apple", "Banana", "Cherry", "Date", "Elderberry"]
override func viewDidLoad() {
super.viewDidLoad()
// 3) Assign the data source and delegate
tableView.dataSource = self
tableView.delegate = self
// 4) Set the reuseIdentifier for your cell
tableView.register(UITableViewCell.self, forCellReuseIdentifier: "FruitCell")
}
}
Here’s what we did:
- Added an IBOutlet for the Table View.
- Created the fruits array, so we actually have content to display.
- Assigned
tableView.dataSource = selfandtableView.delegate = selfso our view controller will supply data and handle user interactions.
4. How to Use Delegate and Data Source for Each
4.1. UITableView (Fruits Example)
We now adopt the UITableViewDataSource and UITableViewDelegate protocols in FruitsViewController:
extension FruitsViewController: UITableViewDataSource {
// Tells how many rows to display in each section
func tableView(_ tableView: UITableView, numberOfRowsInSection section: Int) -> Int {
return fruits.count
}
// Creates (or reuses) and configures each cell
func tableView(_ tableView: UITableView, cellForRowAt indexPath: IndexPath) -> UITableViewCell {
// Dequeue using the reuse identifier we set in the XIB
let cell = tableView.dequeueReusableCell(withIdentifier: "FruitCell", for: indexPath)
cell.textLabel?.text = fruits[indexPath.row]
return cell
}
}
extension FruitsViewController: UITableViewDelegate {
// Called when a user taps a row
func tableView(_ tableView: UITableView, didSelectRowAt indexPath: IndexPath) {
print("Selected fruit:", fruits[indexPath.row])
tableView.deselectRow(at: indexPath, animated: true)
}
}
- Data Source:
numberOfRowsInSection: The count isfruits.count.cellForRowAt: Dequeues a reusable cell named"FruitCell"and sets the label tofruits[indexPath.row].
- Delegate:
didSelectRowAt: Handles user taps. Here, we simply print the selected fruit.
Result: A functional table showing our fruits list.
4.2. UICollectionView (Color Example)
We’ll create another view controller named ColorGridViewController for a grid of colored cells.
Add the .xib + Swift Class
- File → New → File from Template
- Cocoa Touch Class, name it
ColorGridViewController, fromUIViewControllertemplate. - Open
ColorGridViewController.xib, select the top-level view → set Class toColorGridViewController.
Drag a UICollectionView
- In the XIB, search “Collection View.”
- Drag it to the main view. Pin edges with constraints..
Create IBOutlet
@IBOutlet weak var collectionView: UICollectionView!
Configure in viewDidLoad()
import UIKit
class ColorGridViewController: UIViewController {
@IBOutlet weak var collectionView: UICollectionView!
// For demonstration: an array of UIColors
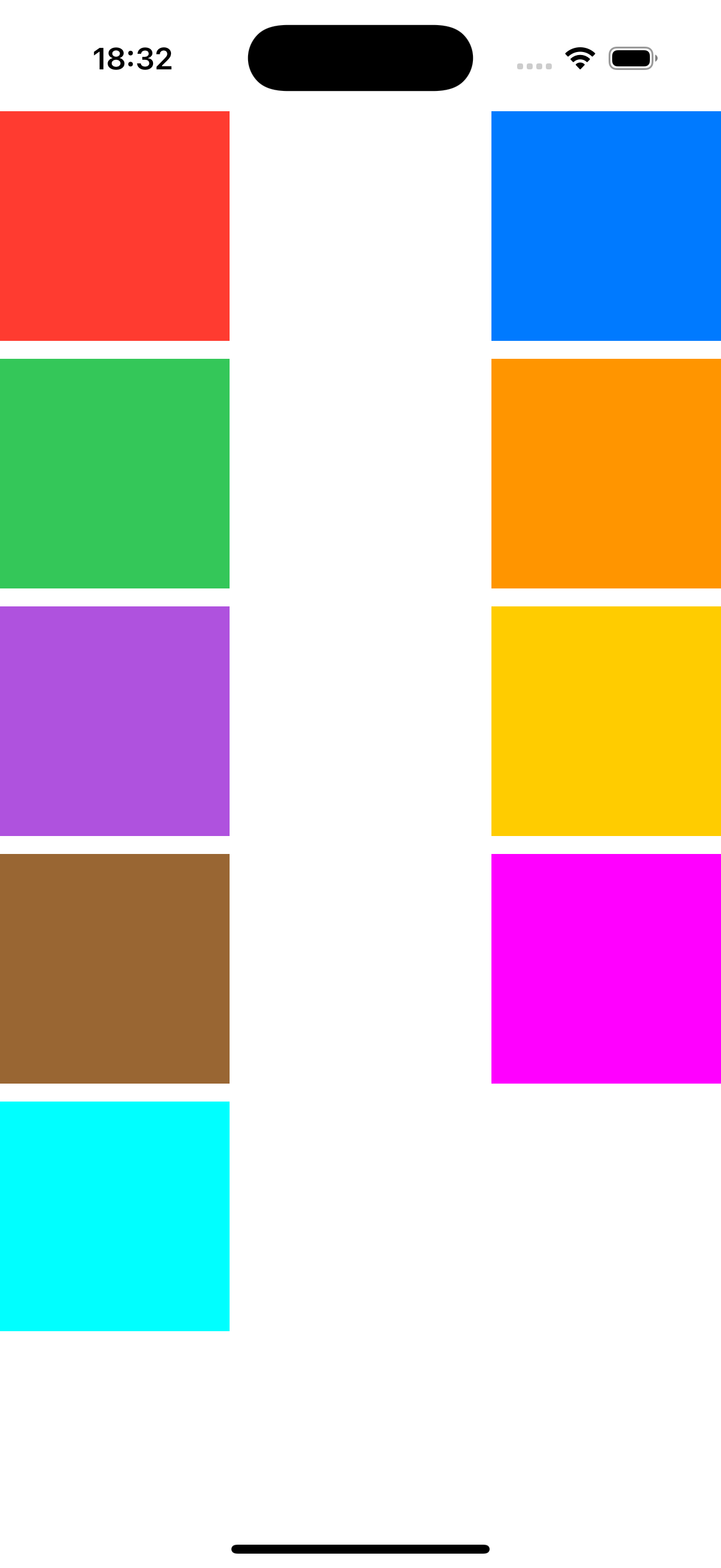
private let colors: [UIColor] = [
.systemRed, .systemBlue, .systemGreen,
.systemOrange, .systemPurple, .systemYellow,
.brown, .magenta, .cyan
]
override func viewDidLoad() {
super.viewDidLoad()
// Assign data source & delegate
collectionView.dataSource = self
collectionView.delegate = self
// Register the dequeue cell
collectionView.register(UICollectionViewCell.self, forCellWithReuseIdentifier: "ColorCell")
}
}
Adopt Data Source & Delegate
extension ColorGridViewController: UICollectionViewDataSource {
// Number of items
func collectionView(_ collectionView: UICollectionView, numberOfItemsInSection section: Int) -> Int {
return colors.count
}
// Create/reuse each cell
func collectionView(_ collectionView: UICollectionView, cellForItemAt indexPath: IndexPath) -> UICollectionViewCell {
let cell = collectionView.dequeueReusableCell(withReuseIdentifier: "ColorCell", for: indexPath)
cell.backgroundColor = colors[indexPath.item]
return cell
}
}
extension ColorGridViewController: UICollectionViewDelegate {
// Called when user taps a cell
func collectionView(_ collectionView: UICollectionView, didSelectItemAt indexPath: IndexPath) {
print("Tapped color at index:", indexPath.item)
}
}
Now you have a basic collection view that displays colored cells.

5. How to Create Custom Cells
5.1. Custom UITableViewCell
If you want a row to show, say, an image and a label, you can create a separate XIB for the cell:
- File → New → File… → Cocoa Touch Class
- Subclass
UITableViewCell, name itFruitTableViewCell. - Check “Also create XIB” if possible, or create the XIB separately.
- Subclass
- In
FruitTableViewCell.xib:- Click the top-level cell. In the Identity Inspector, set Class =
FruitTableViewCell. - Place a UILabel and an UIImageView in the cell.
-
Create IBOutlets in
FruitTableViewCell.swift:@IBOutlet weak var fruitImageView: UIImageView! @IBOutlet weak var fruitNameLabel: UILabel! - Set the reuseIdentifier to
"FruitCell"in the Attributes Inspector.
- Click the top-level cell. In the Identity Inspector, set Class =
-
In
FruitsViewController.viewDidLoad(), you can register this XIB if you’re not using the same XIB prototype cell:let nib = UINib(nibName: "FruitTableViewCell", bundle: nil) tableView.register(nib, forCellReuseIdentifier: "FruitCell") -
Use it in
cellForRowAt:func tableView(_ tableView: UITableView, cellForRowAt indexPath: IndexPath) -> UITableViewCell { let cell = tableView.dequeueReusableCell(withIdentifier: "FruitCell", for: indexPath) as! FruitTableViewCell cell.fruitNameLabel.text = fruits[indexPath.row] // cell.fruitImageView.image = ... return cell }
5.2. Custom UICollectionViewCell
Similar approach:
- Subclass
UICollectionViewCell. - Create a XIB.
- Add UI elements (label, image, etc.), link IBOutlets.
- Register or use a prototype cell with that custom class/reuse ID.
6. Custom Collection Layouts
UICollectionView supports:
- Flow Layout + Delegate: A standard grid or list that you can tweak (row spacing, item spacing, item size, etc.).
-
Implement
UICollectionViewDelegateFlowLayout:extension ColorGridViewController: UICollectionViewDelegateFlowLayout { func collectionView(_ collectionView: UICollectionView, layout collectionViewLayout: UICollectionViewLayout, sizeForItemAt indexPath: IndexPath) -> CGSize { let spacing: CGFloat = 10 let totalWidth = collectionView.bounds.width let itemWidth = (totalWidth - spacing) / 2 return CGSize(width: itemWidth, height: itemWidth) } } -
This achieves a 2-column layout with minimal code.
-
- Fully Custom Layout: Subclass
UICollectionViewLayoutorUICollectionViewFlowLayoutto create advanced designs (like Pinterest-style masonry).
For most scenarios, a flow layout with delegate methods is enough.
7. Conclusion
Following these steps, you can:
- Add a UITableView or UICollectionView into a XIB.
- Connect them via IBOutlets and set the reuse identifier in the prototype cell.
- Configure them in code by assigning
dataSourceanddelegate. - Implement the necessary methods for each protocol:
- UITableViewDataSource / UITableViewDelegate
- UICollectionViewDataSource / UICollectionViewDelegate
- Create custom cells when you need more than a simple label.
- Customize layouts in UICollectionView, either with flow layout or a custom approach.
With this knowledge, you can build scrollable, high-performance lists and grids in your iOS apps. Whether you need a simple table of fruits or a dynamic 2-column gallery, UITableView and UICollectionView are powerful foundations to get the job done!
8. Homework
- Implement the UI for the Browse and Favorites screen;
- Browse should use a 2-column UICollectionView;
- Favorites should use a UITableView;